
Scientific name
Species name
Mass
Wingspans
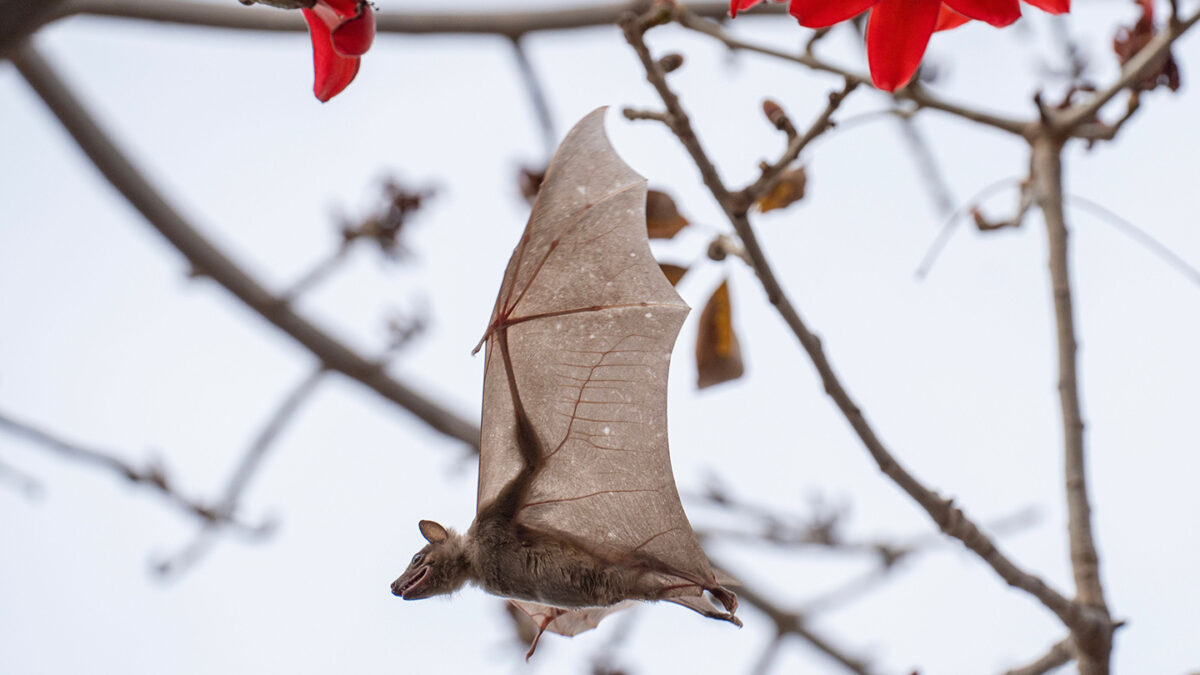
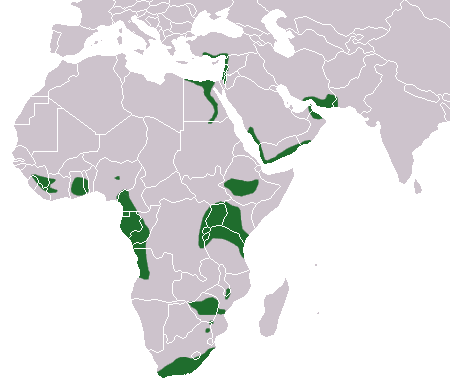
The Egyptian fruit bat or Egyptian rousette (Rousettus aegyptiacus) is a species of megabat that is found in Africa, the Middle East, the Mediterranean, and the Indian subcontinent. Egyptian fruit bats have a distinctive appearance, with a fox-like face and large, pointed ears. They have reddish-brown fur on their backs and lighter-colored fur on their underbellies.
They are named for their diet, which consists mainly of fruit, but they also eat nectar, flowers, and pollen. Individuals are dark brown or grayish brown, with their undersides paler than their backs. These bats are highly social animals and are known to roost in large groups, sometimes numbering in the thousands.

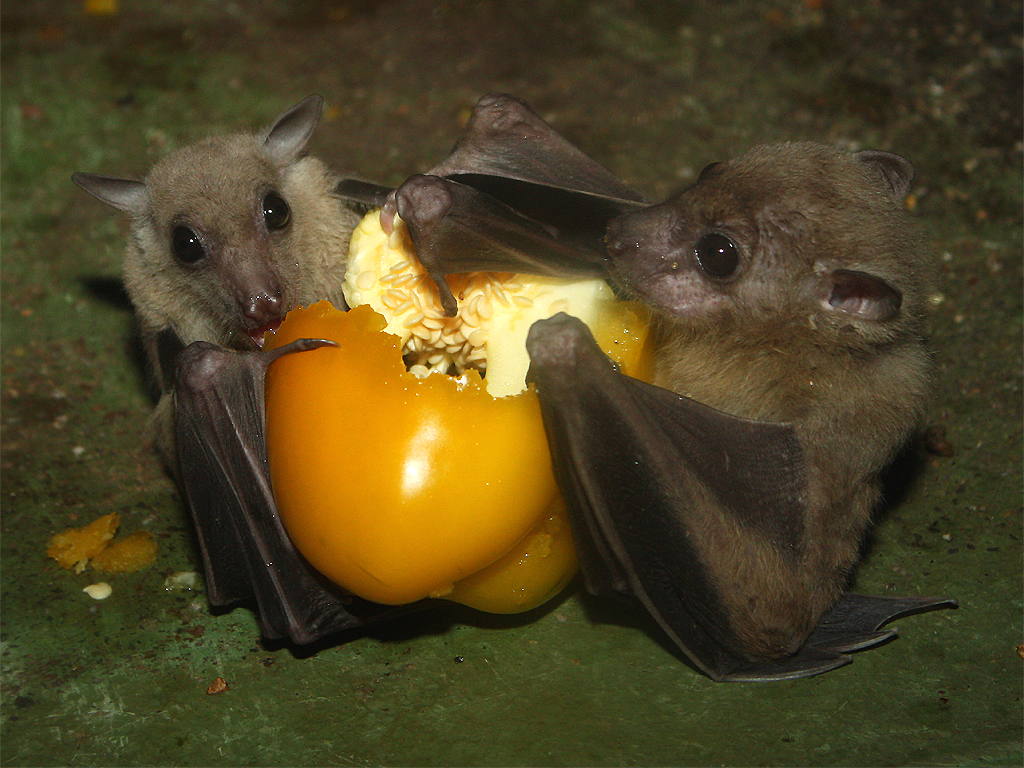
The Egyptian fruit bat is a frugivore that consumes a variety of fruits depending on the season and local availability. Because of its consumption of commercially-grown fruits, the Egyptian fruit bat is considered a pest by farmers. Egyptian fruit bats play an important role in pollination and seed dispersal for many plant species. They are also preyed upon by a variety of predators, including birds of prey and snakes.

The Egyptian fruit bat, also known as the Egyptian rousette, is a species of bat that is found in various parts of Africa and the Middle East, including Egypt, Sudan, Tanzania, and Yemen.
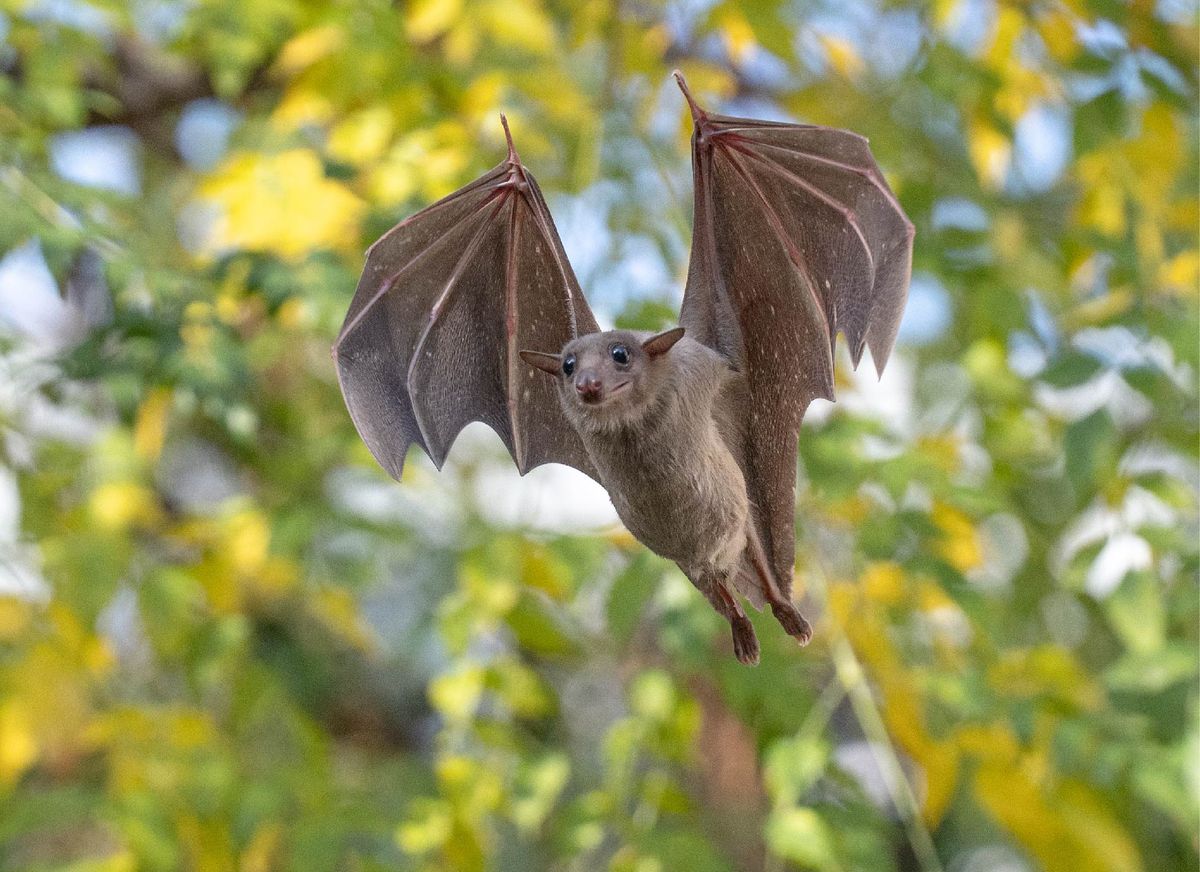
The Egyptian fruit bat has one of the greatest ratios of brain weight to body weight of any bat species. It is well adapted to seeing in low light and possesses a highly developed sense of smell. The regions of the brain associated with sight and smell are similarly well-developed. Its eyes are large and well-developed, while its ears are considered medium-length.

